Automated Phased Array Testing
Phased array testing and imaging, one of the most advanced means of ultrasonic testing method used in modern NDT science. It is becoming quite common and well-rounded ultrasonic testing technique, designed to increase flaw delectability and to perform ultrasonic C-scan inspection on the fly. Phased array technology offers means to focus the ultrasonic beam at different locations and steer it to reach flaws at hidden parts of industrial structures, hence, substantially reducing the scanning time and simplifying the inspection pattern by scanning electronically in milliseconds instead of scanning mechanically in a few seconds.
When inspection cycle time and defect/data interpretation represent important factors, phased arrays are usually combined with automated multi-axis scanning systems creating powerful and fast ultrasonic inspection solution. Such solution is rapidly becoming as popular for many NDT applications and especially for weld testing and aerospace applications where ultrasonic inspection systems with rapid and reliable flaw detection are required.
- Phased array immersion tank
- Phased array-Gimbal/Gimbal
Phased array inspection of composites
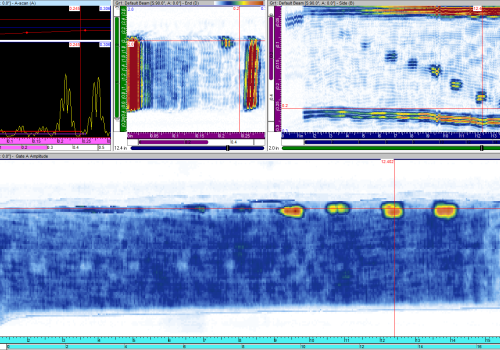
Automated immersion system with phased array was designed to inspect aerospace composite parts. Linear and curved arrays are used to rapidly cover the inspection of the entire part. This turnkey solution consists of an ultrasonic immersion scanner, a phased array instrument and an array probe, TecView™ software with contour following capabilities for motion control and phased array data acquisition, management and analysis. Amplitude and time-of-flight C-scans are presented below from composites curved radii test sample with known defects. Three sections of the sample were tested: straight section, curved and inner radius section. The following tests were performed on the curved section and on the ID inner radius section. The flat and curved sections were inspected with 0 degree 64 elements linear array, however, the inner radius section was inspected with curved linear arrays of 64 elements. The automated immersion scanner provided constant array to sample-water path and accurate array positioning, aligning the ultrasonic beams at 90 degrees to the part surface and allowing complete inspection of the sample.
- Curved radii sample
- Scan of curved section
Conclusions
Combining the phased array probes and the motion accuracy of the automated immersion scanner, an optimized and complete ultrasonic inspection solution was created. This automated phased array solution provided a rapid inspection setup with few array passes.
Applications which require rapid coverage of large areas, inspection solutions for slightly curved geometries or relatively increased ultrasonic penetration can all be met with an automated phased array scanners could meet these challenges. However, for parts with more complex geometries; parts with complicated curvatures and surfaces as well as free form shapes that do not have any axis of symmetry, automated tridimensional dimensional scanning solution would be a better option.